Icosahedron
An icosahedron is the dual of a dodecahedron: each dodecahedron face center becomes a vertex; the three centers around each original dodecahedron vertex become one triangle.
Steps:
- Find every dodecahedron face center.
- Normalize those centers to the unit sphere → 20 vertices.
- Group the three centers around each original dodecahedron vertex (corner) → 20 faces.
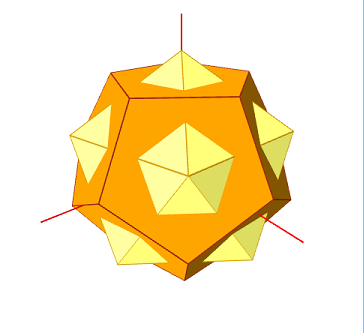
The yellow icosahedron appears if you remove the orange reference dodecahedron.
Add the icosahedron module
src/lib.rs additions:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; // ...keep earlier functions through dodecahedron... pub mod icosahedron; // add this pub use icosahedron::icosahedron; // add this }
Construct Main Function
src/icosahedron.rs:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; /// Icosahedron via dual of a dodecahedron. pub fn icosahedron() -> PolygonMesh { //PLACE STEPS 1-5 HERE } }
Step 1: Start from a dodecahedron
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let dodeca: PolygonMesh = crate::dodecahedron(); let d_positions = dodeca.positions(); }
Step 2: Build vertex positions from face centroids
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let positions: Vec<Point3> = dodeca .face_iter() .map(|face| { let centroid = face .iter() .map(|v| d_positions[v.pos].to_vec()) .sum::<Vector3>(); Point3::from_vec(centroid.normalize()) }) .collect(); }
How this block builds icosahedron vertices
dodeca.face_iter()iterates over each pentagonal face of the source dodecahedron.- For each face we grab its five vertex positions from
d_positions, convert them to vectors, and sum them to get the face centroid vector. centroid.normalize()projects that centroid direction onto the unit sphere so every new vertex sits on radius 1.Point3::from_vec(...)turns the normalized direction back into a point; collecting the results gives the 20 icosahedron vertex positions.
Step 3: Build faces by collecting touching centroids
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let mut faces: Faces = (0..20) .map(|i| { dodeca .face_iter() .enumerate() .filter(|(_, f)| f.contains(&i.into())) .map(|(idx, _)| idx) .collect::<Vec<usize>>() }) .collect(); }
How this block builds icosahedron faces
- We iterate over each of the 20 original dodecahedron vertices (
0..20), because every dodeca vertex becomes one icosahedron face. - For a given dodeca vertex
i, we scan all dodeca faces withface_iter().enumerate()and pick the ones that contain that vertex (f.contains(&i.into())). - The indices of those touching faces are collected into a
Vec<usize>; these indices correspond to the centroids computed earlier (which are now icosahedron vertices). - Gathering all 20 such lists yields the 20 triangular faces of the icosahedron.
Step 4: Fix winding so normals point outward
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { faces.face_iter_mut().for_each(|face| { let p: Vec<Point3> = face.iter().map(|v| positions[v.pos]).collect(); let center = p[0].to_vec() + p[1].to_vec() + p[2].to_vec(); let normal = (p[1] - p[0]).cross(p[2] - p[0]).normalize(); if center.dot(normal) < 0.0 { face.swap(0, 1); } }); }
How this block orients face winding
- For each face we fetch its three vertex positions (
p). - We sum the three position vectors to get a rough face center direction (
center); no division needed because only direction matters. - We compute the face normal via the cross product of two edges and normalize it.
- If the normal points inward (
center.dot(normal) < 0), we swap two vertices to flip the winding so the normal points outward.
Step 5: Construct the mesh
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { PolygonMesh::new( StandardAttributes { positions, ..Default::default() }, faces, ) }
Export the icosahedron
Add examples/icosahedron.rs:
use truck_meshalgo::prelude::NormalFilters; fn main() { let mut mesh = truck_meshes::icosahedron(); mesh.add_naive_normals(true); // optional, for shading truck_meshes::write_polygon_mesh(&mesh, "output/icosahedron.obj"); }
Run it:
cargo run --example icosahedron
View it
Open output/icosahedron.obj in your preferred OBJ file viewer. You should see a single icosahedron.
gif below from Bambu Studio.

File tree after this step
truck_meshes/
├─ Cargo.toml
├─ src/
│ ├─ lib.rs
│ ├─ triangle.rs
│ ├─ square.rs
│ ├─ tetrahedron.rs
│ ├─ hexahedron.rs
│ ├─ octahedron.rs
│ ├─ dodecahedron.rs
│ └─ icosahedron.rs
├─ examples/
│ ├─ triangle.rs
│ ├─ square.rs
│ ├─ tetrahedron.rs
│ ├─ hexahedron.rs
│ ├─ octahedron.rs
│ ├─ dodecahedron.rs
│ └─ icosahedron.rs
└─ output/ # exported OBJ files (e.g., output/icosahedron.obj)
Full code:
src/lib.rs:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; pub fn write_polygon_mesh(mesh: &PolygonMesh, path: &str) { let mut obj = std::fs::File::create(path).unwrap(); obj::write(mesh, &mut obj).unwrap(); } pub mod triangle; pub use triangle::triangle; pub mod square; pub use square::square; pub mod tetrahedron; pub use tetrahedron::tetrahedron; pub mod hexahedron; pub use hexahedron::hexahedron; pub mod octahedron; pub use octahedron::octahedron; pub mod dodecahedron; pub use dodecahedron::dodecahedron; pub mod icosahedron; pub use icosahedron::icosahedron; }
src/icosahedron.rs:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; pub fn icosahedron() -> PolygonMesh { let dodeca: PolygonMesh = crate::dodecahedron(); let d_positions = dodeca.positions(); let positions: Vec<Point3> = dodeca .face_iter() .map(|face| { let centroid = face .iter() .map(|v| d_positions[v.pos].to_vec()) .sum::<Vector3>(); Point3::from_vec(centroid.normalize()) }) .collect(); let mut faces: Faces = (0..20) .map(|i| { dodeca .face_iter() .enumerate() .filter(|(_, f)| f.contains(&i.into())) .map(|(idx, _)| idx) .collect::<Vec<usize>>() }) .collect(); faces.face_iter_mut().for_each(|face| { let p: Vec<Point3> = face.iter().map(|v| positions[v.pos]).collect(); let center = p[0].to_vec() + p[1].to_vec() + p[2].to_vec(); let normal = (p[1] - p[0]).cross(p[2] - p[0]).normalize(); if center.dot(normal) < 0.0 { face.swap(0, 1); } }); PolygonMesh::new( StandardAttributes { positions, ..Default::default() }, faces, ) } }
examples/icosahedron.rs:
use truck_meshalgo::prelude::NormalFilters; fn main() { let mut mesh = truck_meshes::icosahedron(); mesh.add_naive_normals(true); // optional, for shading truck_meshes::write_polygon_mesh(&mesh, "output/icosahedron.obj"); }