First Triangle
Add the triangle module to lib.rs
src/lib.rs (root exports + helper):
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; /// Write any mesh to an OBJ file. pub fn write_polygon_mesh(mesh: &PolygonMesh, path: &str) { let mut obj = std::fs::File::create(path).unwrap(); obj::write(mesh, &mut obj).unwrap(); } pub mod triangle; //add this pub use triangle::triangle; //add this }
Explanation of pub mod and pub use
pub mod triangle;
mod triangle;loads thetriangle.rsfile as a module in the crate.- Making it
pubexposes that module so other files or external crate can access its contents.
pub use triangle::triangle;
use triangle::triangle;imports thetriangle()function into the crate root.- Making it
pubre-exports the function so users can calltruck_meshes::triangle()without the module path.
Construct Main Function
src/triangle.rs:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use std::iter::FromIterator; use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; /// A single equilateral triangle in the XY plane. pub fn triangle() -> PolygonMesh { //PLACE STEP 1-4 HERE } }
Step 1: Define vertex positions
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let positions = vec![ Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), //vertex index: 0 Point3::new(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), //vertex index: 1 Point3::new(0.5, f64::sqrt(3.0) / 2.0, 0.0), //vertex index: 2 ]; }
Explanation
Create three Point3 coordinates that form an equilateral triangle on the XY plane. Two points sit on the X axis at y = 0, and the third is centered at x = 0.5 (midway between the base points) with y = sqrt(3)/2 so all sides are length 1. These positions are the raw vertex data the mesh will consume.
Step 2: Build attribute set
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let attrs = StandardAttributes { positions, ..Default::default() }; }
Explanation
Store the vertex positions in the StandardAttributes struct, which is where a mesh stores all vertex-level attributes (positions, normals, UVs, etc.). We will only set positions, and leave every other attribute at its default.
Step 3: Define mesh faces
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let faces = Faces::from_iter([[0, 1, 2]]); }
Explanation
Define the triangle by listing the indices of its three vertices. Their counter-clockwise order (0 → 1 → 2) sets the face orientation, marking the triangle’s front side as facing the +Z direction.
Face orientation (important)
- CCW order (counter-clockwise) → face points toward you
- CW order (clockwise) → face points away
When looking at the outside, list triangle vertices counter-clockwise.
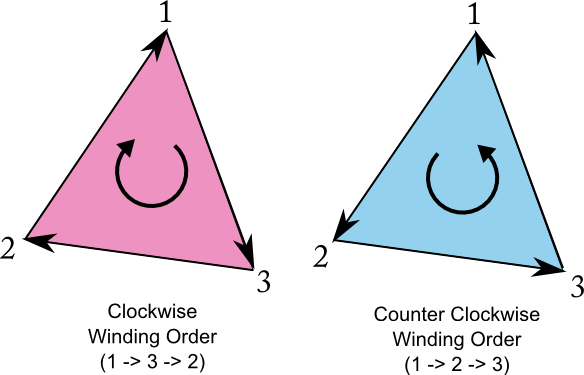
Step 4: Construct the mesh
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { PolygonMesh::new(attrs, faces) }
Explanation
Construct the mesh by passing the vertex attributes attrs and the face index list faces to PolygonMesh::new. Each face index (like [0, 1, 2]) points into the attribute array, telling the mesh which positions belong to that face.
The counter-clockwise order of these indices establishes the face orientation, which renderers use for lighting, backface culling, and generating smooth shading. PolygonMesh::new combines these into a fully defined mesh ready for rendering or OBJ export.
Export the triangle
Add a tiny example at examples/triangle.rs:
fn main() { let mesh = truck_meshes::triangle(); truck_meshes::write_polygon_mesh(&mesh, "output/triangle.obj"); }
Run it:
cargo run --example triangle
View it
Open output/triangle.obj in Preview/3D Viewer/ParaView/Blender. You should see a single triangle.
Image below from ParaView.

File tree after this step
truck_meshes/
├─ Cargo.toml
├─ src/
│ ├─ lib.rs
│ └─ triangle.rs
├─ examples/
│ └─ triangle.rs (optional helper to export)
└─ output/ # exported OBJ files (e.g., output/triangle.obj)
Full code:
src/lib.rs:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; pub fn write_polygon_mesh(mesh: &PolygonMesh, path: &str) { let mut obj = std::fs::File::create(path).unwrap(); obj::write(mesh, &mut obj).unwrap(); } pub mod triangle; pub use triangle::triangle; }
src/triangle.rs:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use std::iter::FromIterator; use truck_meshalgo::prelude::*; pub fn triangle() -> PolygonMesh { let positions = vec![ Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), Point3::new(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), Point3::new(0.5, f64::sqrt(3.0) / 2.0, 0.0), ]; let attrs = StandardAttributes { positions, ..Default::default() }; let faces = Faces::from_iter([[0, 1, 2]]); PolygonMesh::new(attrs, faces) } }
examples/triangle.rs:
fn main() { let mesh = truck_meshes::triangle(); truck_meshes::write_polygon_mesh(&mesh, "output/triangle.obj"); }